1.2.1. Colour Models
A colour model is a mathematical model describing how colours can be represented by sequences of numbers. These numbers are referenced to a certain colour space. There are many different colour spaces in use. In this lesson, we will concentrate only on the colour space which is mainly used to display colours on a computer monitor.
RGB Colour Space
In the RGB colour model a colour is represented
by three values, giving the amount of red (R), green (G) and blue (B) light. The
combination of these 3 colours is utilized to create all other colours.
The RGB colour space is an additive colour schema. The primary
colours sum up to white. RGB is a common colour model for computer graphics.
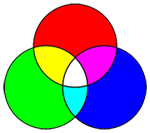 Additive colour space
Additive colour spaceThere are other colour-models, such as HSV (Hue, Saturation, Value or Brightness (HSB)) which is also used in computer graphics or CMY(K) (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black) which is a subtractive colour schema and is used for printing colours. We will not go into their details in this lesson. If you're interested in more information about these and other colour spaces have a look at the GITTA lesson "Colour Design – Colour Models".
Now you know how to create any arbitrary colour by mixing the primary colours Red Green and Blue (in chapter 1.3.4. you will have the possibility to create any arbitrary colour in an interaction part). But if really all possible colours are used to display an image on a screen depends on the colour depth of an image. To understand the correlation between colour depth and the number of used colours in an image, please read the next paragraph.
