1.2.2. URL
You all know very well the World Wide Web. Already by reading this lesson
you are using a Web Browser.
When starting your Web
Browser you do it always with the intention to get some information of the WWW
such as e.g. looking up the timetable of your train, looking up the price of
the
newest computer, etc. This information is stored on various Web Pages, which
are
stored on different Web Servers.
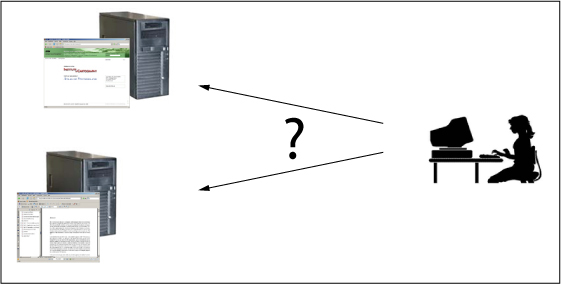 How to access the information which is stored on a Web Server?
How to access the information which is stored on a Web Server?To get the wanted information, you have to know the location - the so
called Web-Address - of the web resource and
enter it in the address bar of the browser.
But what is the content of
a Web-Address and how does it look like? The following parts have to be defined
in the Web-Address when accessing a Web Page :
- The method of how to access the Web Server. Therefore, the type of protocol that is used has to be specified.
- The name of the computer where the resource is stored.
- The resource that we are looking for.
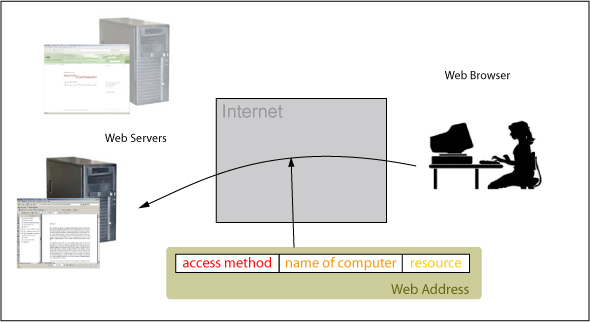 A Web Server can be accessed using a Web Address
A Web Server can be accessed using a Web AddressDomain Name System (DNS)
All computers and all files on the computers are identified by means of names. All names that can be found in the Internet are organised in a worldwide list of names the so called Domain Name System (DNS). The structure of the DNS is like the one of a tree as it is shown below. Each node of the tree represents a Domain and therefore a part of the Internet names. The node "Root" represents the whole Internet. Each Domain can be subdivided into several Sub-Domains. A Web Server is always part of a Domain. A Domain in turn, may contain several Web-Servers. (BADACH et al. 2003, p. 16-17)
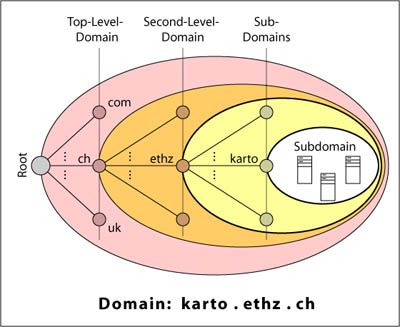 Domain Name System
Domain Name SystemTo identify the resources in the Internet a so called URL (Uniform Resource Locator) was defined that has to be entered in the address bar of the browser.
An URL may look like this:
http://www.ika.ethz.ch:80/teaching/mmkarto
The role of all these components are the followings:
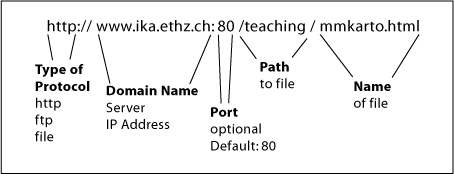 URL
URL- Type of Protocol: is used for the communication,
- Domain Name (Host): is used to know with whom is communicated,
- Network Port on the Server: is the access point on the server for data entry or exit,
- Path: gives the path to the resource on the server,
- Nameof file.
The Domain Name can be replaced by the IP address of the
server: the URL would then look like this:
http://129.132.127.159:80/teaching/mmkarto
Query Strings
In addition to the path where the wanted file is
stored, URLs can be extended by query strings. To understand what is meant by
this we want you to do a little exercise:
- Open a new browser window and type the following address in the address bar: http://www.google.ch/search?q=cartouche&q=e-learning
- Press the "Enter key" and look what happens.
Without having started the Google homepage and without having entered the
two terms "Cartouche" and "E-Learning" in the search bar we get the
corresponding matches. Why this?
We entered the query for these terms
already in the URL by using the query string
"?q=cartouche&q=e-learning". The query starts with a question mark "?"
and is followed of one or a series of parameter=value pairs (in our case this
is
"q=cartouche" and "q=e-learning"). The series of pairs is seperated by the
ampersand "&". The presented query can therefore be extended by an
arbitrary number of pairs.
Not every web page supports query strings in the URL. Programs that allow the execution of queries within the URL, have to be implemented on the web server.
Exercise
Try to create other queries by changing the values of
the parameter q and adding other parameter=value pairs of the above query string
"http://www.google.ch/search?q=cartouche&q=e-learning". Look at the
result you get in your browser.
You can discuss your
results on the discussion board "Internet Techniques", if you want.
