Link to MenuLink to Table Of Content
- AT&T:
- "AT&T (formerly an abbreviation for American
Telephone and Telegraph) is an American telecommunications company. AT&T
provides voice, video, data, and Internet telecommunications and professional
services to businesses, consumers, and government agencies." (WIKIPEDIA)
- Byte:
- A byte comprises 8 bits. Since one bit can adopt two states it is
possible to describe 256 (28) signs with one
byte.
- Client:
- Typically, a client is an application that runs on a personal
computer or workstation and relies on a server to perform some operations. For
example,
an e-mail client is an application that enables you to send and receive e-mail. (BAER)
- Colour Gradient:
- Colour gradient is a smooth blending of shades from light
to dark or from one colour to another.

- Hyperlink:
- An element in an electronic document that links to another
place in the same document or to an entirely different document. Typically, you
click on
the hyperlink to follow the link. (Panama-Hosting.com) It is most commonly used
in the World Wide Web to link various documents (Web Pages, pdf-files, etc.).
- Hypertext:
- Hypertext is text with links to other text. Documents written
as hypertext contain text that when "clicked on" by the user with a mouse, links
to
other documents. (Texas A & M University)
- Java:
- Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language developed
by Sun Microsystems. It is similar to C++, but has been simplified to eliminate
language
features that cause common programming errors. Java is a general purpose programming
language with a number of features that make the language well suited for use on
the
Web. Small Java applications are called Java applets and can be downloaded from
a Web
server and run on your computer by a Java-compatible Web Browser such as Mozilla
Firefox or Opera. (BAER)
- MCI:
- MCI, Inc. is an American telecommunications company headquartered in
Ashburn, Virginia. (WIKIPEDIA)
- MIME:
- MIME (Multipart Internet Mail Extension) is a standard specifying
the format of data transferred over the Internet. (JS-X.com) MIME allows
to specify the transferred content (Content-Type). For example when html pages
are
transmitted the MIME-Type is text/HTML.
- Network:
- A network is a group of two or more things or people. This notion
is often used in terms of "computer network", where computer systems are linked
together
so that they can exchange data and share resources.
- Paletted Image:
- A paletted image is a method to store a raster graphic. If
an image has 256 colours or less, a colour palette is used to encode all colours.
A code
number is assigned to every colour used in the image. The colour palette is stored
separated from the pixel image. For each pixel is set the code number of the colour
palette instead of the real colour code. Since the code number (e.g. 255) needs
less
storage space as the real colour code (e.g. 255,255,255) the storage space of the
whole
image is reduced. (WIKIPEDIA)
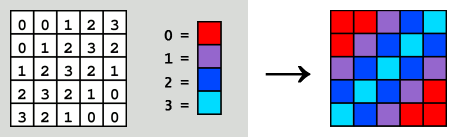 (WIKIPEDIA)
(WIKIPEDIA)
- Server:
- A server is a computer or device on a network that manages network
resources. For example, a file server is a computer and storage device dedicated
to
storing files. Any user on the network can store files on the server. A print server
is
a computer that manages one or more printers, and a network server is a computer
that
manages network traffic. A database server is a computer system that processes
database
queries. Servers are often dedicated, meaning that they perform no other tasks
besides
their server tasks. On multiprocessing operating systems, however, a single computer
can
execute several programs at once. A server in this case could refer to the program
that
is managing resources rather than the entire computer. (BAER)
- Sprint:
- Sprint Nextel Corporation is one of the largest telecommunications
companies in the United States. It operates the third largest wireless network
in the
U.S. with nearly 44 million subscribers. (WIKIPEDIA)
- Transparency:
- Transparency defines the ability of an object to allow light
to pass through it. Therefore a transparent object is one that can be seen through.
- User Interface:
- The system of computer screen images, devices, and
software components that allow the user to interact with and control the computer’s
operating system. Graphical user interfaces (GUI) allow the user to interact with
the
operating system by manipulating icons or menus. Command-line interfaces allow
the user
to interact with operating systems by entering commands from the keyboard. (ATC)
- W3C (World Wide Web Consortium):
- The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is
the international standards body and develops interoperable technologies
(specifications, guidelines, software, and tools) to lead the Web to its full potential
as a forum for information, commerce, communication, and collective
understanding. (ETV Cookbook)
- XForms:
- XForms is a W3C specification for the description of forms and form elements
in XML. More infos: http://www.w3.org/MarkUp/Forms/
- XHTML:
- XHTML is the next generation of HTML and is a hybrid between HTML
and XML. XML was designed to describe data. HTML was designed to display data.
XHTML is
much stricter than HTML. Not all browers support XML so XHTML provides an intermediary
solution and can be interpreted by XML and HTML browsers. (DevLib - Devices and Development)
- XML:
- XML is a text-based markup language for data interchange on the Web.
As with HTML, you identify data using tags (identifiers enclosed in angle brackets,
like
this: <price>12.95</price>). Collectively, the tags are
known as "markup". But unlike HTML, XML tags label the structure of the data, rather
than specifying how to display it. (Data Direct Technologies)
- XUL:
- XUL (XML User Interface Language) is a Mozilla project for the description of forms
and form elements
in XML. XUL will be mostly used in Mozilla applications, such as the browser Firefox
and mail client Thunderbird.



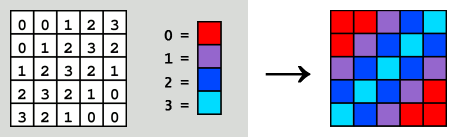 (WIKIPEDIA)
(WIKIPEDIA)