1.3.4. XML Attributes
XML elements can have attributes in the start tag. They are used to
provide additional information about elements.
Attributes
often provide information that is not a part of the data. In the example below,
the file type is irrelevant to the data, but important to the software that
wants to manipulate the element:
 XML Attribute
XML AttributeAttributes values must always be enclosed in quotes, but either single or double quotes can be used:
 XML Attribute with double quotes
XML Attribute with double quotes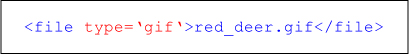 XML Attribute with single quotes
XML Attribute with single quotesUse of elements versus attributes
Data can be stored in child elements or in attributes.
 Information stored as attribute
Information stored as attribute Information stored as element
Information stored as elementIn the first example the sex is an attribute. In the last, sex is a child element. Both examples provide the same information.
There are no strict rules whether to use attributes or child elements. It is recommended though to use elements to describe data itself and attributes only for metadata (information that describes the data).
Exercise
Imagine you want to store the data of a map in an XML document. Which
elements have to be included in this document and how should the structure of
these elements look like?
Possible elements could be: map scale, width
and height of the map, projection, legend, title, subtitle, relief and other
map
layers, etc.
Create an XML document that includes all elements that
are needed for a map. Which elements are included as attributes and which ones
as elements? Hand in your XML document to your tutor.
