1.2.2. XML in 3 Points
The following summary in three points is taken out of a W3C Homepage and attempts to capture enough of the basic concepts to enable you to see the advantages of XML.
- XML is for structuring
data
Structured data includes things like spreadsheets, address books, technical drawings, etc.
 Spreadsheet Spreadsheet |
 Address Book Address Book |
 Technical Drawing, © GIS-Fachstelle Kanton Basel-Landschaft (Kanton Basellandschaft (CH)) Technical Drawing, © GIS-Fachstelle Kanton Basel-Landschaft (Kanton Basellandschaft (CH)) |
- XML is a set of rules (you may also think of them as guidelines or conventions) for designing text formats that let you structure your data. XML is not a programming language, and you do not have to be a programmer to use it or learn it. XML makes it easy for a computer to generate data, read data, and ensure that the data structure is unambiguous. XML is extensible, platform-independent, and it supports internationalization and localization.
- XML looks a bit like
HTML
Like HTML, XML makes use of tags (words bracketed by '<' and '>') and attributes (of the form name="value"). While HTML specifies what each tag and attribute means, and often how the text between them will look in a browser, XML uses the tags only to delimit pieces of data, and leaves the interpretation of the data completely to the application that reads it. In other words, if you see "<p>" in an XML file, do not assume it is a paragraph. Depending on the context, it may be a price, a parameter, a person ... (and who says it has to be a word with a "p"?).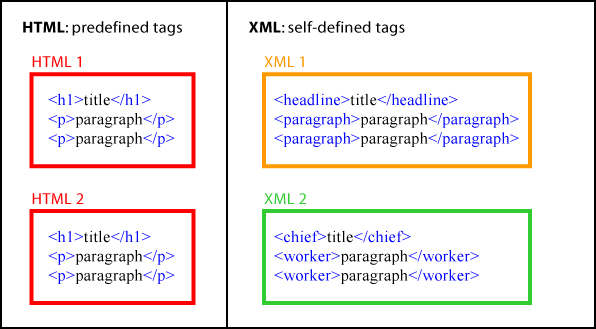 HTML tags versus XML tags
HTML tags versus XML tags - XML is text, but is not meant to be
read
Like HTML, XML files are text files that people should not have to read, but may when the need arises. One advantage of a text format is that it allows people, if necessary, to look at the data without the program that produced it; that means, you can read a text format with your favourite text editor.
Compared to HTML, the rules for XML files allow fewer variations. A forgotten tag, or an attribute without quotes makes an XML file unusable, while in HTML such practice is often explicitly allowed.
