1.3.3. Examples
A - Adaption to user preferences
Adaption has been applied in practise in a number of varied and novel ways. In the CRUMPET project (Schmidt-Belz et al. 2003) researchers looked at how tourists could benefit from the provision of sight-seeing information. They adapted the information content according to the context of the user`s personal preferences for different types of information and their current location.
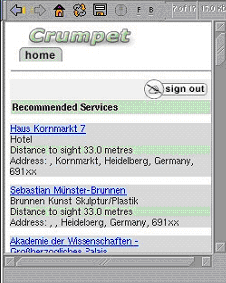 Example search results from the CRUMPET project with respect to personal preferences (Schmidt-Belz et al. 2003)
Example search results from the CRUMPET project with respect to personal preferences (Schmidt-Belz et al. 2003)B - Adaption to seasons of a year and to user age
In the GiMoDig project (Nivala et al. 2003) researchers used the contexts of the user, the time of year and the purpose of use to adapt the content and presentation of maps. For example icon styles were varied according to the age of the user, and different recreational activities were shown at different times of the year.
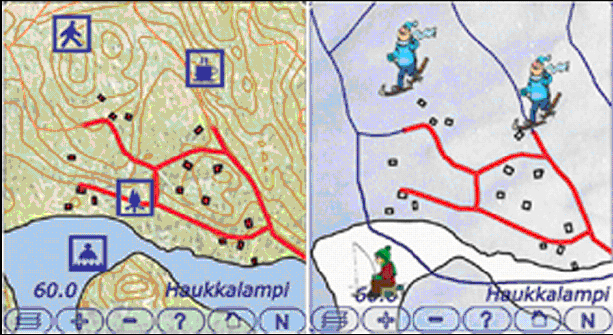 Maps adapted to for the GiMoDig project ( Nivala et al. 2004)
Maps adapted to for the GiMoDig project ( Nivala et al. 2004)C - Adaption to location and social context
(2002) and (2002) both looked at how location and social context could be used to help guide new students on a university campus. Their systems adapted the information contents according to location, time of day and social relationship between students and student groups. The contents consisted of virtual notes left by students at locations anywhere in the university, which would pass on information, experiences and preferences about what goes on where and when at that note's location.
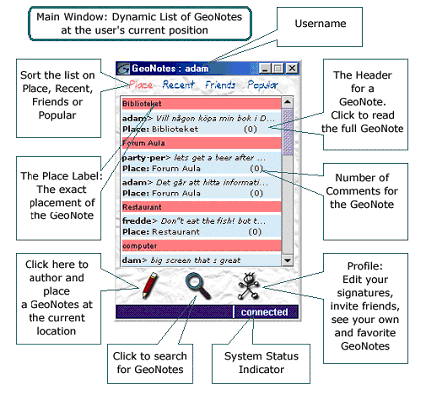 A virtual note (Persson et al. 2002)
A virtual note (Persson et al. 2002)D - Adaption to system context
(2004) used the system context to adapt the content and presentation of information. They designed a cat-and-mouse type multiplayer game where players could use dead spots in the network and GPS coverage to hide from other players.
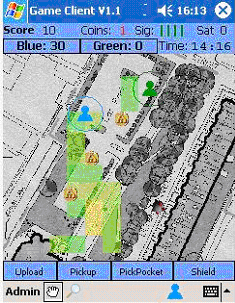 A seamful game (Chalmers et al. 2004)
A seamful game (Chalmers et al. 2004)