1.2.2. Examples
Categories of location based services
There exist a broad range of different location based services. The following animation gives an overview on the main categories of LBS applications and names some examples. For every example additionally information on the positional accuracy needs and the service type (push or pull service) is shown. This listing does not claim to be complete and is certainly growing over time.
The different service categories differ in the needed ![]() accuracy, the
accuracy, the ![]() environment they are used in and the
information
environment they are used in and the
information ![]() delivery. High positional
accuracy denotes an accuracy within 50 meter while a low accuracy is worse than
300 meter.
delivery. High positional
accuracy denotes an accuracy within 50 meter while a low accuracy is worse than
300 meter.
Given below is a bunch of LBS applications. Have a 5 minutes view on some of them to get a deeper impression of the possibilities which LBS delivers.
A - Emergency Services
One of the most evident applications of LBS is the ability to locate an individual who is either unaware of his/her exact location or is not able to reveal it because of an emergency situation (injury, criminal attack, and so on). E.g. motorists are often unaware of their exact location when their vehicle breaks down. With the exact location automatically transferred to the emergency services the assistance can be provided quickly and efficiently. This category includes public and private emergency services for both pedestrians and drivers. While public emergency services for calling out fire-fighters, medical teams, etc., are currently being mostly regulated by public organisations the emergency roadside assistance for drivers appears to be one of the most promising of the assistance services in terms of operator revenue.
A 1 - Enhanced 911 (E911) mandate (Click here for more information)
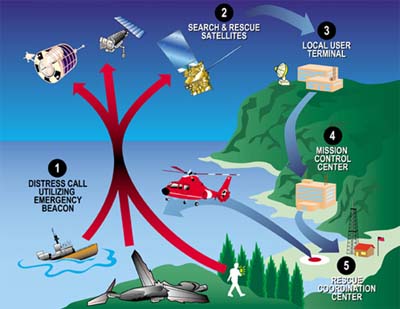
A 2 - SAR – Search and Rescue (Click here for more information)
A 3 - Automotive assistance and theft protection
Automotive assistance and theft protection: Some upper class car manufacturer offer already special automotive assistance via LBS. In case of a car breakdown or an emergency the car driver can directly call via the on-board computer the emergency service and transmit his actual position. Some systems already foresee even a transmission of the error analysis by the on-board systems. Other systems foresee the transmission of the cars actual position in the case that it gets stolen. It is only a matter of time that all these systems will be available for all cars.
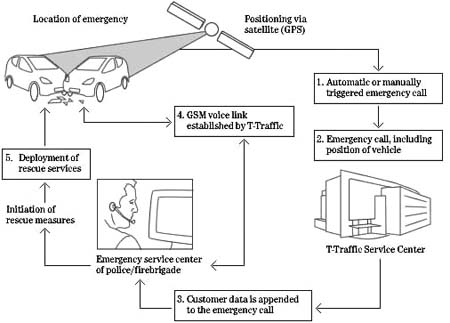 Mercedes-Benz TELEAID (T-Traffic)
Mercedes-Benz TELEAID (T-Traffic)B - Navigation Services
Navigation services are based on mobile users. Needs for directions within their current geographical location. The ability of a mobile network to locate the exact position of a mobile user can be manifested in a series of navigation-based services:
B 2 - Traffic management (Click here for more information)
B 3- Car-park guidance systems (Click here for more information)
B 4 - Indoor routing (Click here for more information)
C - Information Services
Finding the nearest service, accessing traffic news, getting help with navigating in an unfamiliar city, obtaining a local street map – these are just a few of the many location based services. Location-sensitive information services mostly refer to the digital distribution of information based on device location, time specificity and user behaviour. The following types of services can be identified within this category:
C 1 - Travel services / tourist guides
Travel services / tourist guides: Services such as guided tours (either automated or operator-assisted), notification about nearby places of interest (monuments etc.), transportation services, and other services that can be provided to tourists moving around in a foreign environment (city, national park).
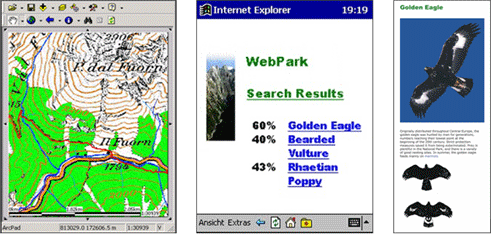 WebPark LBS with presentation of habitats of different plants and animals (Edwardes et al. 2003)
WebPark LBS with presentation of habitats of different plants and animals (Edwardes et al. 2003)C 2 - Mobile yellow pages (Click here for more information)
C 3 - Travel planer for train, bus etc. (Click here for more information)
C 4 - Infotainment services (Click here for more information)
C 5 - Shopping guides (Click here for more information)
C 6 - Mobile blackboards (Click here for more information)
D - Advertising Services
Furthermore, mobile advertising has gained significant attention because of the unique attributes, such as personalization, that offer new opportunities to advertisers to place effective and efficient promotions on mobile environments. There are various mechanisms for implementing mobile advertising coupled with LBS. Examples are mobile banners, alerts (usually dispatched as SMS messages) and proximity triggered advertisements. Due to the potentially intrusive nature of mobile advertising services, it is generally acknowledged that users will have to explicitly register to receive such services perhaps in exchange for other benefits.
D 1 - Location aware SMS advertising
Location aware SMS advertising: SMS messages with advertising for nearby events or offers. Subscriber of such services get reimbursement. E.g. for each received SMS the user gets points which he can exchange against other bonuses.
E - Tracking and Management Services
Tracking services can be equally applicable both to the consumer and the corporate markets. One popular example refers to tracking postal packages so that companies know where their goods are at any time. Vehicle tracking can also be applied to locating and dispatching an ambulance that is nearest to a given call. A similar application allows companies to locate their field personnel (for example, salespeople and repair engineers) so that they are able, for example, to dispatch the nearest engineer and provide their customers with accurate personnel arrival times. Finally, the newfound opportunity to provide accurate product tracking within the supply chain offers new possibilities to mobile supply chain management (m-SCM) applications (Kalakota et al. 2001).
E 1 - People tracking
People tracking: E.g. for children or elderly people. Child locator services allow the parents to locate their children via a secured web-site. The child therefore wears a special GPS watch.
E 2 - Integration of LBS for field support in CRM (Click here for more information)
E 3 - Monitoring services for fleets of vehicles or individuals (Click here for more information)
E 4 - Infrastructure or facility management (Click here for more information)
F - Billing Services
Location-sensitive billing refers to the ability of a mobile location service provider to dynamically charge users of a particular service depending on their location when using or accessing the service.
F 1 - Operator Services (Click here for more information)
F 2 - Toll systems
Toll systems: A toll system that is capable of calculating and collecting road use charges based on the distance travelled. The automated tracking ensures that the collection of road tolls does not disrupt traffic flow.
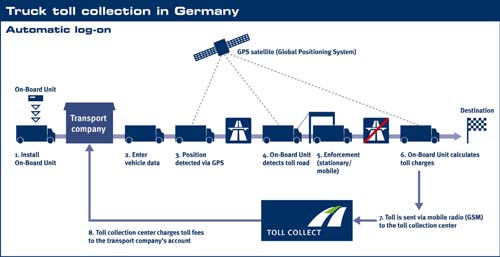 Truck toll collection in Germany (Toll Collect)
Truck toll collection in Germany (Toll Collect)G - Games and Leisure
Tracking services can be equally applicable both to the consumer and the corporate markets. As far as similarly, tracking services can be effectively applied in corporate situations as well. One popular example refers to tracking vehicles so that companies know where their goods are at any time. Vehicle tracking can also be applied to locating and dispatching an ambulance that is nearest to a given call. A similar application allows companies to locate their field personnel (for example, salespeople and repair engineers) so that they are able, for example, to dispatch the nearest engineer and provide their customers with accurate personnel arrival times. Finally, the newfound opportunity to provide accurate product tracking within the supply chain offers new possibilities to mobile supply chain management (m-SCM) applications (Kalakota et al. 2001).
G 1 - Buddy finder / group management
Buddy finder / group management: These applications allow mobile users to locate friends, family, co-workers, or other members of a particular group that are within close range and thus, create virtual communities of people with similar interests.
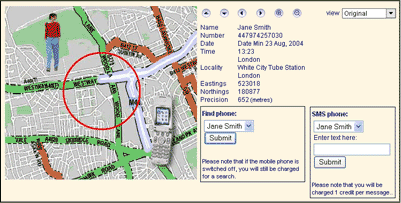 Mobile Phone Tracking (Trace a Mobile.com)
Mobile Phone Tracking (Trace a Mobile.com)G 2 - Geocaching (Click here for more information)
G 3 - Mobile games (Click here for more information)
More examples can be found at http://www.in-duce.net/archives/locationbased_mobile_phone_games.php
H - Outlook - Augmented Reality
In the next decade, researchers plan to pull graphics out of the phone or computer display and integrate them into real-world environments. This new technology, called augmented reality, will further blur the line between what's real and what's computer-generated by enhancing what we see, hear, feel and smell. Other than in virtual environments, in augmented reality, the user can see the real world around him, with computer graphics superimposed or composed with the real world. Instead of replacing the real world it is supplemented. So called "see-through" devices, usually worn on the head, overlay graphics and text on the user's view of his or her surroundings.
 Augmented Reality (How Stuff Works)
Augmented Reality (How Stuff Works)