1.4.4. Positioning
In the previous section, which described the general information workflow, a positioning service has been introduced to obtain the user location. We will now give a short introduction to positioning methods. A more detailed discussion is done in the Unit Networks & Positioning of the Lesson Techniques for LBS Cartography.
If we do not consider the manual input of the position as a location
method a general classification of positioning methods can be done into two
groups: The first group is called network-based
positioning. Here, a tracking and evaluation of the user
location is done by using the base station network (see image A). Using this
technique either the mobile device is sending a signal or the device is "sensed"
by the network. The position is calculated by the control stations of the
network.
The second positioning group is called terminal-based positioning. In this case the
location is calculated by the user device itself from signals received from base
stations. A well know example for a terminal-based system is the location
determination by use of the Global Positioning System (GPS), and also Galileo
in several years. The base stations
for the GPS system are the GPS-satellites (see image B in the Figure). Finally
a
third group of positioning techniques emerges from combination of network and
terminal positioning techniques.
The basic principle for the calculation of the user position, valid for all groups, is:
- Base Stations have a known position.
- Information from a signal is transformed into distances (N.B.: this is not valid for Angle Of Arrival (AOA) technique).
- Using the obtained distances (device - base station x) as circle radius around the base station. Obtaining the position from the arc intersection (see image A)
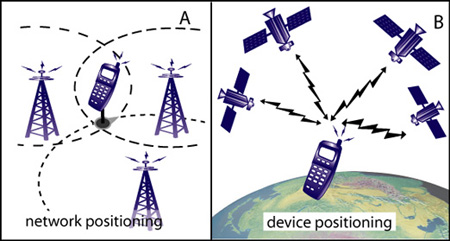 Types of positioning and basic principle. The
currently two most common position technologies are the already mentioned GPS
and the position evaluation using the Cell-ID from the nearest base transceiver
station, a network method. Whereas GPS delivers a very accurate position
(accuracy up to 5m) does the Cell-ID deliver a very coarse position (accuracy
between 100m to 30 km). Especially GPS is (currently) an outdoor positioning
method. To obtain indoor positions with high accuracy, as needed for instance
in
museums or shopping malls, localisation methods based on WLAN, Bluetooth or
infrared technologies should be applied. In general it is important to note that
the position technology and its accuracy influences the application of different
location based services (see also application examples in Unit 2).
Types of positioning and basic principle. The
currently two most common position technologies are the already mentioned GPS
and the position evaluation using the Cell-ID from the nearest base transceiver
station, a network method. Whereas GPS delivers a very accurate position
(accuracy up to 5m) does the Cell-ID deliver a very coarse position (accuracy
between 100m to 30 km). Especially GPS is (currently) an outdoor positioning
method. To obtain indoor positions with high accuracy, as needed for instance
in
museums or shopping malls, localisation methods based on WLAN, Bluetooth or
infrared technologies should be applied. In general it is important to note that
the position technology and its accuracy influences the application of different
location based services (see also application examples in Unit 2).
