1.1.3. LBS Keywords
LBS applications can be characterized by a number of keywords and related questions:
- Mobile User:
 Who or what is mobile? The mobile object can be a person or a
device like a car navigation system. (see further How
is it useful? and (2004))
Who or what is mobile? The mobile object can be a person or a
device like a car navigation system. (see further How
is it useful? and (2004))
- Mobile Activities:
 What Questions and Problems have users? Such questions
do emerge from the user actions: locating, navigating, searching, identifying,
event
check. A further question with respect to actions is the (spatial) scope of activities.
According to (2004) we can distinguish
three types of spatial scope:
What Questions and Problems have users? Such questions
do emerge from the user actions: locating, navigating, searching, identifying,
event
check. A further question with respect to actions is the (spatial) scope of activities.
According to (2004) we can distinguish
three types of spatial scope:
- Macro scale: Do I need an overview?
- Meso scale: What is reachable for me?
- Micro scale: Where am I?
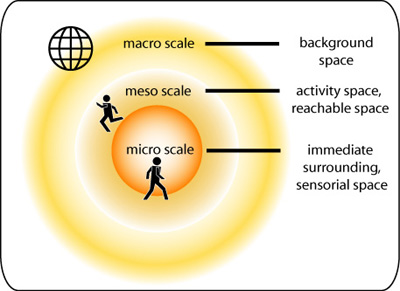 The spatial scope of activities. (Heidmann et al. 2003)
The spatial scope of activities. (Heidmann et al. 2003)- Information:
 What is needed to answer a user question and how is it done?
A model of information retrieval is needed to answer the user questions. Such an
information process model contains a model of possible questions, defines Queries
of
geographic base data and location information data, and specifies possible answers
(see
animation below).
What is needed to answer a user question and how is it done?
A model of information retrieval is needed to answer the user questions. Such an
information process model contains a model of possible questions, defines Queries
of
geographic base data and location information data, and specifies possible answers
(see
animation below).
- Search and Spatial Analysis:
 Which methods and algorithms are suitable
for real-time information query in the Internet and spatial data analysis? Further
question are: ”How to integrate data and information of different scale, quality,
data
types, prices?" "How is the data availability and actuality?"
Which methods and algorithms are suitable
for real-time information query in the Internet and spatial data analysis? Further
question are: ”How to integrate data and information of different scale, quality,
data
types, prices?" "How is the data availability and actuality?"
- User Interface:
 Is a person using a PDA or mobile phone or something
else? How can the user or (navigation) system formulate his needs and can make
them more
concrete after obtaining an overview?
Is a person using a PDA or mobile phone or something
else? How can the user or (navigation) system formulate his needs and can make
them more
concrete after obtaining an overview?
- Visualisation:
 How is the information, returned from LBS, communicated to
the user? Speech, text, pictures, pictograms, maps, lists,..
How is the information, returned from LBS, communicated to
the user? Speech, text, pictures, pictograms, maps, lists,..
- Technology:
 How are service requests and data transferred between user
and service provider? Where are the data stored? Which services are provided? Which
positioning technology is used? ...
How are service requests and data transferred between user
and service provider? Where are the data stored? Which services are provided? Which
positioning technology is used? ...
These questions and characteristics will be considered in more detail in the following units and lessons.
The Information Process
The animation below shows the cartographic information process if a user asks for shops or restaurants close to his position. Moving the slider from left to right will give you the processing stages of the result map.
Question and answer model for cartographic information processes adapted adapted from Heidmann 1999